B.U.M.E.S Optimization and Vision Integration
Background
B.U.M.E.S (Boston University Manufacturing Execution Software) is a fully automated system for manufacturing and assembling a cord organizer (also known as a cordganizer), consisting of two distinct parts:
● Lid Piece (1.5” x 3” x 0.25” Polycarbonate)
● Base Piece (1.5” x 3” x 1” HDPE)
The goal of this project:
-
Optimize BUMES by integrating Lean principles to increase throughput, reduce waste and defects.
-
Utilize vision system as a post-manufacturing process that automatically identifies and sorts machined parts into specified categories.
Success will be measured by reductions in defect rates, waste, and cycle time, leading to a more efficient and scalable manufacturing process.


Technical Details
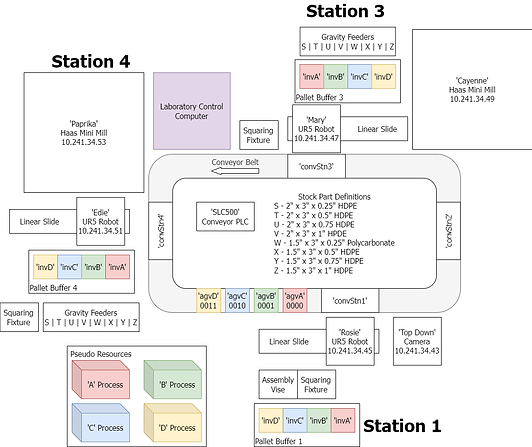
The lab plan view on the right features three UR robots (Rosie, Mary, and Edie), two CNC machines (Cayenne and Paprika), and a conveyor belt, all of which are at the core of the manufacturing process.
Currently, the cycle time for two cordganizers (2 lids and 2 bases) is 25 minutes.

Aim 1: CAD/ CAM Optimization
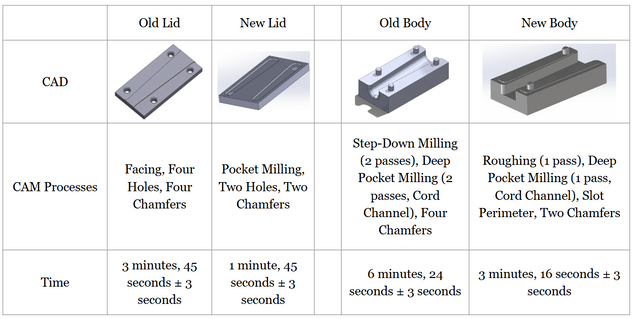
-
Changes in Lid and Body CAD
-
Changed from 4 to 2 holes/pegs
-
Added a snap fit feature to lock them in place
-
-
Changed in Lid and Body CAM
-
Increased tool feed rate
-
Performed single pass runs
-
Decreased number of tool change
-
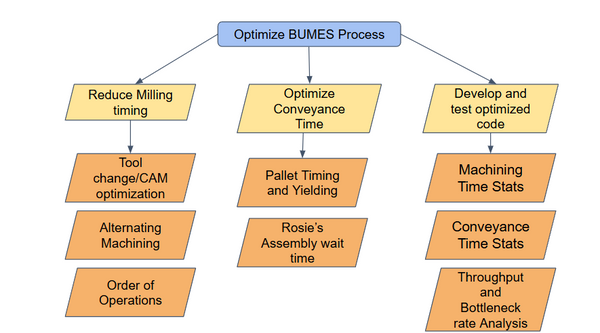
Aim 2: BUMES Process
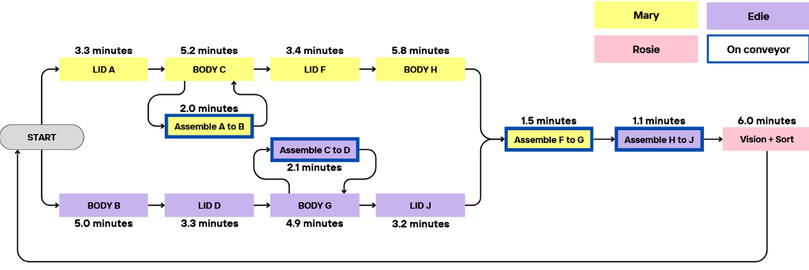
-
1 BUMES cycle → 4 cordganizers + vision + sorting
-
Total time: 24.6 minutes
-
-
13 individual programs to achieve system optimization
-
Lids and bodies are individually called from A to J (excluding E and I) to minimize confusion in the script
-
Eliminate the third robot (Rosie) by performing assembly on conveyor
-
Alternate machining between the two CNCs
-
Could run infinitely after including Vision in the BUMES process
-
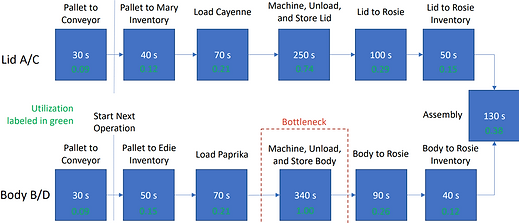
All UR waypoints are optimized to reduce NVAT
-
Before
After


Aim 3: Vision-Based Part Identification and Sorting
-
Added blue tape to some of the lids before production
-
Developed UR scripts to control part handling, positioning, and interaction with the vision system
-
Implemented a vision system to classify and sort Cordganizers based on paint color using camera feedback
-
One of the first groups, that were able to integrate the vision system with the BUMES process


Documentation
BUMES Operation Guide and Supporting Documentation
CAD/CAM Supporting Documentation
Vision Python Scripts Supporting Documentation
Universal Robotics Arms Supporting Documentation
Outcomes/lesson learned
-
Developed an optimized version of the BUMES process by reducing cycle time and increasing throughput.
-
Created new “.urp” files, enabling robots to machine tend, place parts on pallets, and assemble Cordganizers.
-
Reduced milling time by optimizing tool changes in CAD, alternating machining, and using optimal spindle speeds for improved part quality.
-
Identified bottlenecks and NVAT operations, optimized CAM files, and streamlined assembly for greater efficiency.
-
Successfully automated object sorting on a live manufacturing station, improving task execution reliability and adaptability within the BUMES environment.
-
Established communication with robots to sort Cordganizers into their respective bins after manufacturing.
-
Optimize CAM for exclusively snap fit to reduce milling time and tool change
-
Eliminate burring; add finishing passes or decrease milling feed
-
Implement more vision features (size, holes, details etc)
-
Integrate real-time data logging and process tracking to monitor part flow, system performance, and error rates for continuous improvement.
-
Modify the gravity feeders to improve consistency and ensure repeatable part pickup locations for the robot.
-
Implement a cleaning program to remove chips from the work area before part placement in the vise, preventing misalignment and setup errors.
